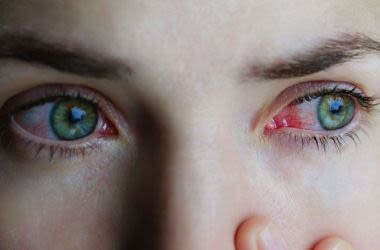
Eye allergies are relatively common. They occur when allergens come into contact with your eyes, causing a reaction. This response is often caused by your immune system failing to process foreign objects and perceiving them as dangerous.
The team at Nicholas Rutkowski, O.D, and Associates can help you relieve eye allergy symptoms such as itchy, red, or watery eyes.
What Causes Eye Allergies?
Allergens are harmless substances. However, if your eyes perceive them as harmful, they will produce histamine to fight them. The histamine may, in turn, trigger symptoms like red eyes and watery eyes. Common airborne allergens include mold, pollen, dust, and pet dander.
Some people may also react violently to eye drops or cosmetics. Identifying your triggers is crucial because you need to avoid them as much as possible.
Ways to Relieve Eye Allergies
Watery, red, or itchy eyes can cause significant discomfort and affect your quality of life. You may have to avoid certain places, objects, or products.
Here are a few approaches to help you alleviate the symptoms of eye allergies:
Avoiding Your Triggers
Your first line of defense is avoidance. You need to limit your exposure to allergens that may trigger a reaction. You can install high-quality filters in your home, wear sunglasses when going outside, roll up your windows when driving, or stay indoors on days when the risk is too high.
Replacing Contacts with Glasses
Allergic patients who wear contact lenses tend to have worse symptoms than those who don’t. This is mainly because airborne allergens can accumulate on the surface of contact lenses. If possible, swap your lenses for glasses during allergy season or talk to your eye doctor about getting disposable contacts.
Eye Drops
Eye drops can tame allergy-related redness, itchiness, and watery. Non-prescription eye drops are sufficient for mild cases, but you should get a prescription if you have severe symptoms. You could also get a recommendation from your doctor on a reliable brand.
Prescription Medication
Sometimes, eye allergy symptoms are too severe to be treated with the methods mentioned above alone. In such cases, your doctor will have to prescribe oral medicines or eye drops to relieve your discomfort effectively. The most common medications employed to treat eye allergies include:
Oral antihistamines: Block histamine from attaching to body cells and causing a reaction
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Minimize symptoms like swelling and inflammation
Decongestants: Relieve red eyes by reducing the size of blood vessels in the eye
Mast cell stabilizers: Used before the start of allergy season to prevent the production of histamine
Corticosteroids: Address more acute eye allergy symptoms
Your doctor may prescribe a combination regimen to achieve the best results.
Allergy Shots
You can get allergy injections for six months once or twice a week, and maintenance shots less regularly after that for five years. You may experience irritation around the site of injection as a side effect.
Immunotherapy
Some doctors recommend immunotherapy for eye allergies that won’t go away. It involves being injected with small doses of allergens to stimulate your body to build up your immunity.
Final Thoughts
There are numerous things you can try at home to help improve your symptoms. However, your doctor will offer the best treatment advice.
If you regularly get eye reactions that are hard to control when exposed to common allergens, schedule a comprehensive eye exam with Dr. Rutkowski and his professional team.