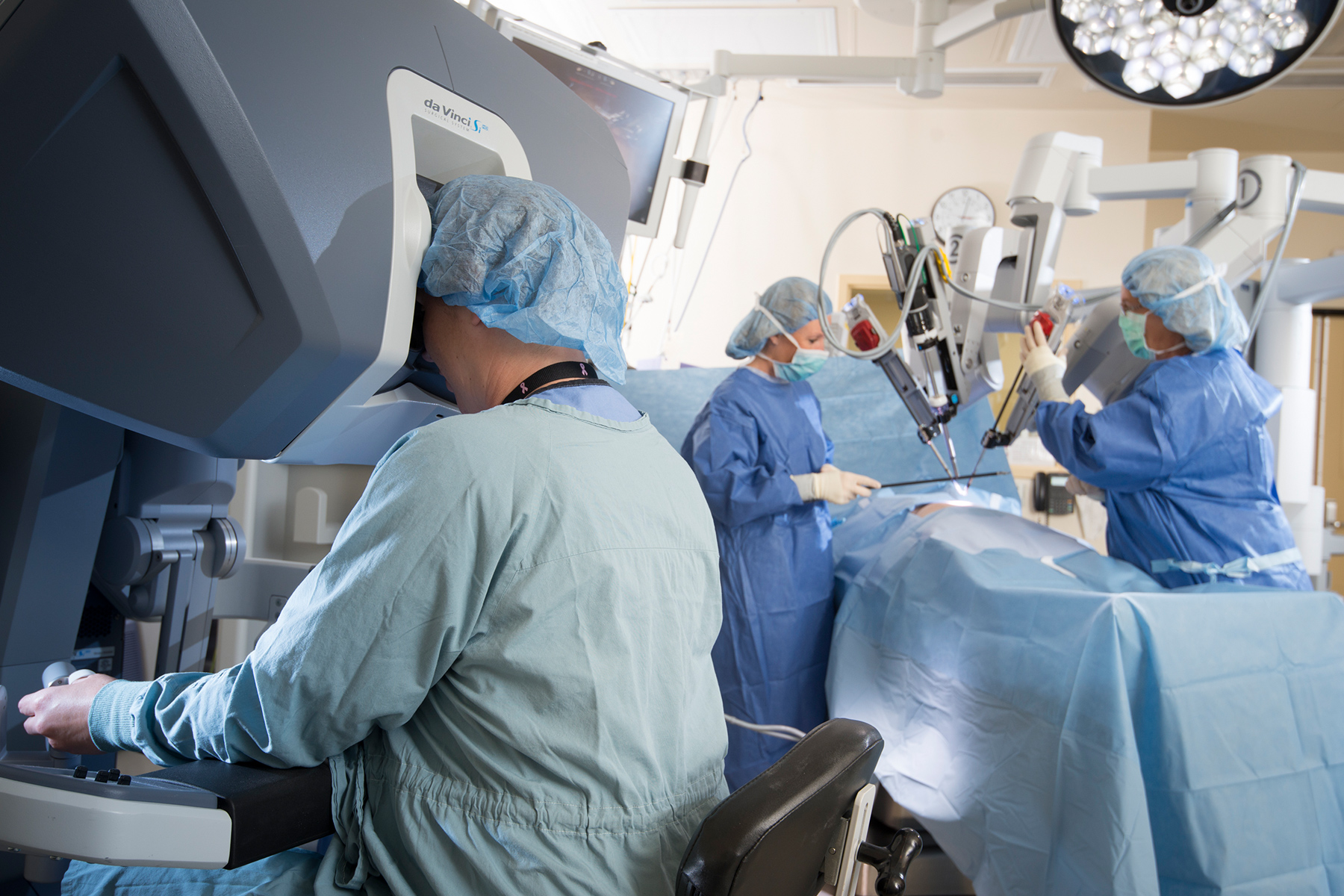
Have you ever wondered how robotic-assisted surgery came to be? Robotic-assisted surgery was first performed in 1985 to assist doctors in achieving a delicate precision using the “Puma 560” robot. There has been an increase in robotic-assisted operations since early 2000, specifically in performing laparoscopies. Darin Swainston, MD, FACOG, has been recognized as one of the top surgeons in the US, with over 1000 successful robotic-assisted surgeries at his Summerlin pelvic pain treatment clinic.
To date, the robotic surgery industry has generated approximately $3 billion in annual revenue. Some of the key players in the robotic surgery industry include CMR Surgical (CMR), Medtronic, Verb Surgical, and Intuitive surgical.
In 2017, studies revealed that close to 2800 hospitals in the US had invested in robotic surgery technology. This was significantly fuelled by the benefits witnessed in operating rooms.
Below is a list of the perceived benefits of robotic-assisted surgery.
Three-Dimensional View of The Operating Field
Surgeons are now more confident when they enter the operating room. Robotic-assisted surgery gives a 3D view of the operating field, which promotes better visualization.
Low Intraoperative Blood Loss
Surgeons are human beings and are, therefore, prone to errors. Surgical robots guarantee movement precision due to zero surgeon tremors. Additionally, robotic-assisted surgery is an accurate and minimally invasive surgery.
Surgeons can also perform complex surgeries on hard to reach areas using snake-like flexible arms. Surgical robots eliminate unnecessary motion that is caused by breathing or when surgeons need to stretch their arms during extended operations.
The small precisions prevent excessive blood loss, unlike conventional open surgery, which would leave large wounds on the patient.
A Shorter Length of Stay (LOS)
A study conducted by one of the key players in the robotic surgery industry revealed that more people are demanding robotic-assisted surgery. With approximately 32% yearly growth in robotic-assisted operation, surgeons estimate a significant increase in not only laparoscopic operations but also robotic gastric, hepatobiliary, pancreatic, and colorectal procedures.
Robotic-assisted surgeries are relatively low risk and less painful. The small precision ensures that there is minimal wound access trauma. Furthermore, there are fewer postoperative complications, less blood loss meaning a quick recovery period. A shorter hospital stay is especially crucial for elderly and obese patients.
Increased Cost Efficacy
Robotic-surgeries will, in the long run, promote cost efficiency. This will be made possible by increasing the number of operations done by surgeons. Furthermore, fewer complications will reduce the length of hospital stay for patients. Overall, it will reduce the number of postoperative surgeries.
You should not that robotic-assisted surgeries tend to be associated with high costs. Public health facilities, for instance, would have to receive a high number of patients for them this procedure to be sustainable. Moreover, public health facilities should already have trained surgeons to prevent additional costs for educating them on how to operate these robots.
Other concerns associated with the use of robots include patent issues, inadequate research to demonstrate patient benefits as well as matters concerning regulatory standards. Experts have, therefore, recommended postoperative assessments to demonstrate the efficacy of robot-assisted surgeries.
Finally, the future of robotic-assisted surgery will require the transformation of five key dimensions, namely: increasing awareness, increasing evidence, promoting innovations, ensuring cost-efficacy and building capacity of both public and private healthcare staff.