Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a disease that has now become common among middle-aged and old individuals. This is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes irritation and swelling of the colon or large intestine. These can be caused by stress or emotional imbalance, abnormal immune systems, genetic factors, environmental factors or an overactive intestinal system. Colorectal cancer is considered to be the third most common cancer diagnosed in both men and women in the world.
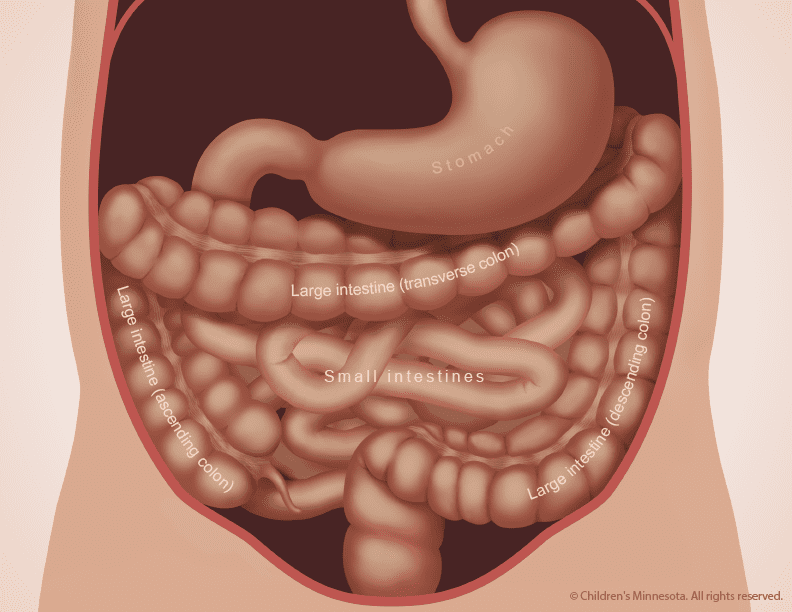
Colectomy or large bowel resection is a surgical treatment in which a part or the whole colon or large intestine is removed. Commonly, there are four types of colectomy. Partial or subtotal colectomy in which part of the colon is removed whereas, in total colectomy, the entire colon is removed. Proctocolectomy is defined as the removal of the large intestine along with the rectum.
In Hemicolectomy, the right or left portion of the colon is removed
On the basis of the diagnosis of the symptoms, specialists recommend any of the above-mentioned surgeries as treatment.
Need-
Colectomy is recommended by doctors in many cases. Excessive bleeding from the large intestine that cannot be controlled and needs surgery on an immediate basis so the affected part can be removed. Bowel obstruction caused by a blocked colon is an emergency that may require a partial or total colectomy. As discussed earlier, at rare times in the early stages of colon cancer a small section needs to be removed using colectomy.
In cases where medication has proven to be ineffective in curing Chron’s disease, colectomy is carried out to provide permanent relief. Another case would be, if the patient is at a very high risk of colon cancer due to the formation of multiple precancerous colon polyps, one may choose to opt for a colectomy.
Procedure-
Preparation-
Doctors instruct their patients a set of rules who are supposed to undergo a colectomy. This set of instructions help in preparing them for the surgery. Certain medications, especially blood thinners, are stopped. Doctors instruct their patients not to eat or drink several hours to a day before the procedure. Doctors also prescribe antibiotics to suppress the bacteria naturally found in the colon so that there is no chance of infection. Drinking a lot of fluids is recommended so that the bowel is entirely cleared. Doctors suggest laxatives that must be mixed with water for easy passing of stool. Doctors also recommend enemas to their patients.
Before initiating the surgical procedure, surgeons provide with some drugs or medicines such as Aminosalicylates, Corticosteroids, Immunomodulators, Biologics, etc to cure the mild pain and some gastric symptoms in the abdomen. The patient is then moved to an operating room and positioned on a table. He or she will be given a general anesthesia medication that induces sleep so that the patient is unable to feel any pain during the operation. The surgical team will then proceed with the colectomy. Colon surgery is generally performed in two ways:
Traditional colectomy. Traditional surgery requires a surgeon to make an incision of about 6 to 8 inches long in the abdominal wall to access the colon. The surgeon uses surgical tools to cut free the intestine from the surrounding tissue and cuts a part of the colon or the entire colon.
Laparoscopic colectomy. In laparoscopic colectomy which is also called minimally invasive colectomy as this involves several small incisions in the abdomen. After that, the surgeon inflates the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide gas through a tube, known as a cannula which helps them to navigate the laparoscope easily. They pass a tiny high-resolution camera through one incision and special surgical tools through the other incisions. The surgeon views a video screen in the operating room as the tools are used to cut the colon from the surrounding tissue. The colon is then brought out through another small incision or port in the abdomen. This process allows the surgeon to operate on the colon outside of the body. Once the colon is repaired, the surgeon reinserts the colon through the incision.
No matter which surgery is carried, the next step is anastomosis. This is to stitch the ends of the colons that are left. If any health portion of the colon is left, surgeons make an opening called a stoma on the outer wall of the belly. The colon is then attached to the outer wall. Stool goes through the stoma into a drainage body that is attached outside the body. The whole method is known as colostomy. A colostomy can either be short-term or permanent.
Risks involved-
The risk of complications is based on the general health of the individual, the type of colectomy he or she is undergoing and the method used by the surgeon to perform the operation.
Generally, risks of colectomy include bleeding, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) which is blood clots in the legs, infection, injury to internal organs near the colon such as the bladder and small intestines, and the tears in the sutures that are used to bandage the remaining parts of the digestive system.
Once the colectomy is complete, doctors ask their patients to limit their consumption of dairy products while they highly suggest the consumption of low fat and high fiber foods such as whole wheat bread, apples, bananas, etc. are recommended. Regularly eating small meals is suggested. The nurses also show how to take care of the wound so that faster recovery is ensured.
